During the 2015 state legislative session, lawmakers considered 514 provisions related to abortion; the vast majority of these measures—396 in 46 states—sought to restrict access to abortion services. This year will be remembered not only because 17 states enacted a total of 57 new abortion restrictions, but also because the politics of abortion ensnared family planning programs and providers as well as critical, life-saving fetal tissue research.
2015 may also be memorable for setting the stage for what is widely anticipated to be one of the most significant Supreme Court rulings on abortion since 1992. In November, the Court agreed to hear a challenge to a Texas law requiring abortion providers to adhere to the standards set for ambulatory surgical centers and to have admitting privileges at a local hospital. At stake is the question of how far states may go in regulating abortion before their actions amount to an unconstitutional “undue burden” on women’s ability to access care. The Court will hear the case in March 2016, with a decision expected in June; it is still considering whether to review a Mississippi admitting-privileges law. (Also in 2016, the Court will revisit the contraceptive coverage guarantee under the Affordable Care Act, weighing its importance and approach against the contention of religiously affiliated employers that they deserve to be entirely exempt from the law.)
At the same time, states made important advances in 2015 on other sexual and reproductive health and rights issues:
- Oregon adopted a measure allowing adults to obtain prescription contraceptives from a pharmacy without first obtaining a prescription.
- The District of Columbia and Oregon adopted measures requiring health plans to allow a woman to obtain a full year’s worth of prescription contraceptives at one time.
- Oregon adopted a measure protecting confidential communications around sensitive health services for individuals covered as dependents under private insurance.
- Maine directed the state to move to expand Medicaid eligibility for family planning services to individuals with an income of up to 209% of the federal poverty level.
- The District of Columbia adopted a provision prohibiting employers from discriminating against employees because of their use, or intended use, of contraceptives, abortion services or fertility treatments.
- Idaho and Maryland adopted measures allowing health care practitioners to provide STI treatment for a patient’s partner without first examining the partner.
- California adopted a measure requiring crisis pregnancy centers and health centers that provide family planning to post information about the availability of free or low-cost pregnancy-related care, including abortion services.
- Four states—Alabama, Arkansas, Maine and Oregon—moved to require that sex education provided in the state include information on violence prevention.
- Illinois and Oregon adopted measures prohibiting “conversion therapy” designed to change sexual orientation as part of mental health treatment for minors.
Access to Abortion Services
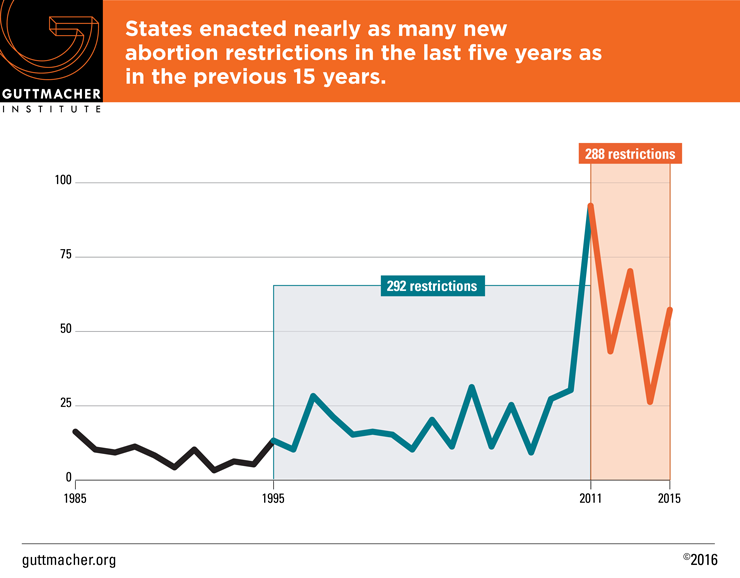
Including the 57 abortion restrictions enacted in 2015, states have adopted 288 abortion restrictions just since the 2010 midterm elections swept abortion opponents into power in state capitals across the country. To put that number in context, states adopted nearly as many abortion restrictions during the last five years (288 enacted 2011–2015) as during the entire previous 15 years (292 enacted 1995–2010). Moreover, the sheer number of new restrictions enacted in 2015 makes it clear that this sustained assault on abortion access shows no signs of abating.
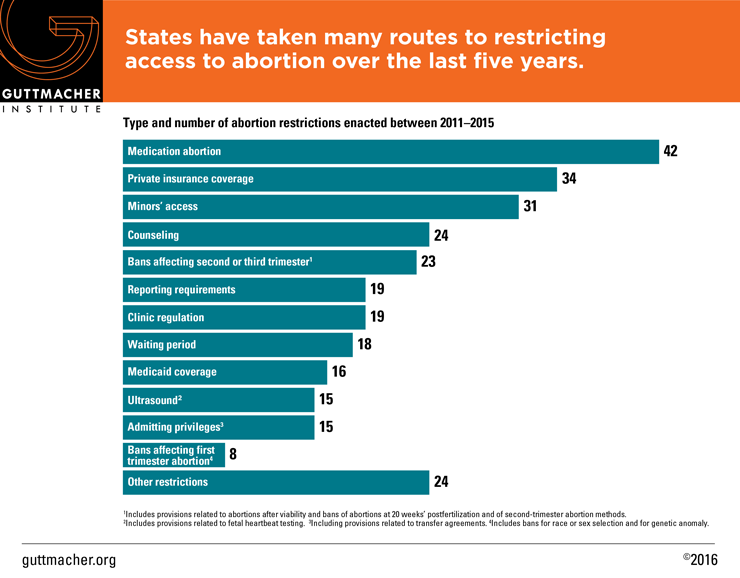
The 288 new restrictions enacted since 2010 include a broad range of approaches, from banning some abortions to putting restrictions on the providers allowed to perform the procedures to limiting insurance coverage.
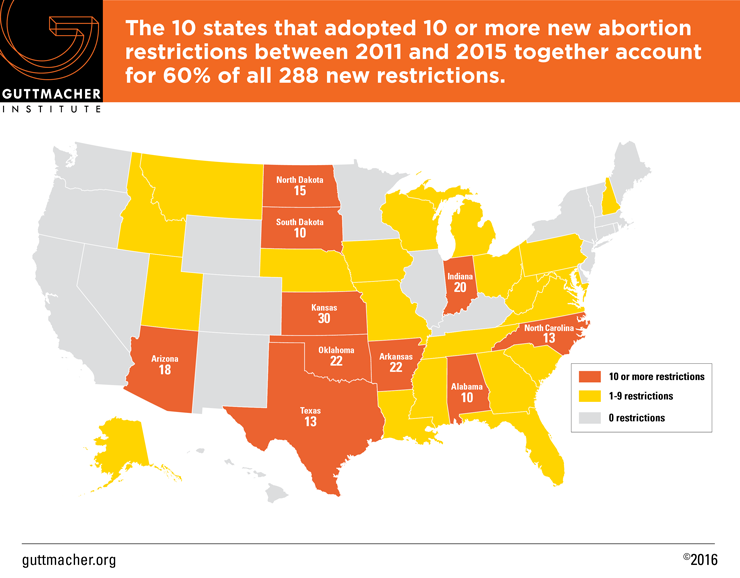
Thirty-one states—spanning all regions of the country—enacted at least one abortion restriction during the last five years. The 10 states that enacted at least 10 new restrictions together account for 173, or 60% of the 288 new abortion restrictions adopted over the last five years. These states are overwhelmingly located in the South and the Midwest, and it is likely that access to services for women in these regions has been impacted significantly. Four states—Arkansas, Indiana, Kansas and Oklahoma—each enacted at least 20 new abortion restrictions, making this handful of states, which together adopted 94 new restrictions, responsible for a third of all abortion restrictions enacted nationwide over the last five years. Kansas has the dubious distinction of leading the pack with 30 new abortion restrictions since 2010.
Although the 57 new abortion restrictions enacted during 2015 include a wide range of provisions, four topics stood out as the subject of particular attention among lawmakers.
- Counseling and Waiting Periods
Five states adopted waiting period legislation in 2015. Florida enacted a 24-hour waiting period, while Tennessee approved a measure mandating a 48-hour wait. Three additional states lengthened existing waiting periods: Arkansas extended the mandatory wait to 48 hours; North Carolina and Oklahoma lengthened the time to 72 hours. (The new Florida law has been temporarily blocked by the courts; the Oklahoma law is also being challenged, but a state court allowed it to go into effect while the case is pending.) Including these new laws, 27 states have waiting periods in effect (see Counseling and Waiting Periods for Abortion).
The new laws in Florida and Tennessee require the woman to receive state-mandated abortion counseling in person, meaning that she must make two separate trips to obtain an abortion. With enforcement of the Florida law blocked, 13 states have two-trip requirements in effect.
- Medication Abortion
Four states sought to use longstanding strategies to restrict access to medication abortion. Arkansas, Idaho and Kansas enacted new measures banning the use of telemedicine for the provision of medication abortion. (A similar measure was vetoed in Montana by Democratic Gov. Steve Bullock.) Arkansas also mandated use of the regimen specified in the FDA-approved labeling, which bans use of the newer evidence-based regimen that is less costly, has fewer side effects and can be used several days later in pregnancy; the law is not in effect due to a court case. Currently, 18 states ban use of telemedicine and three mandate use of the older medication abortion regimen (see Medication Abortion).
Arizona and Arkansas debuted a new approach to discouraging a woman from obtaining a medication abortion. Both states adopted laws requiring doctors to counsel women that the abortion could be stopped if the woman takes a high dose of progesterone after receiving the first of the two drugs included in the medication abortion regimen. According to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, this new approach is based on scant scientific evidence; it relies on a single flawed study of only six cases that did not have oversight by an institutional review board. The Arizona law is blocked pending a legal challenge; the Arkansas law is in effect.
- Abortion After the First Trimester
Abortion opponents unveiled a new strategy in 2015 by moving to ban the use of the procedure used most often for second-trimester abortions. Kansas and Oklahoma both enacted measures to ban this safe and medically proven method that has long been used for abortions after 14 weeks; both laws are enjoined pending court action.
West Virginia and Wisconsin enacted laws banning abortion at or after 20 weeks postfertilization (which is equivalent to 22 weeks after the woman’s last menstrual period). The West Virginia measure is in effect; the one in Wisconsin is slated to go into effect in February. Currently, 12 states (AL, AR, IN, KS, LA, MS, NE, NC, ND, OK, TX, WV) have similar bans in effect (see State Policies on Later Abortions).
- Targeted Regulation of Abortion Providers (TRAP)
Even as the stage was being set for the U.S. Supreme Court to review TRAP laws (see above), legislative action continued apace in several states. Five states adopted TRAP laws in 2015. Following a 2014 ballot initiative that granted lawmakers the ability to enact virtually limitless abortion restrictions, Tennessee enacted a new TRAP law that requires abortion providers to meet the standards that apply to ambulatory surgical centers even though these centers typically provide more invasive and risky procedures than abortion and use higher levels of sedation than commonly provided in abortion clinics.
Arkansas, Indiana, Ohio and Oklahoma made existing requirements more stringent.
- Indiana expanded its existing requirement that surgical abortion providers meet ambulatory surgical center standards to also include facilities that provide only medication abortion. Twenty-four states require abortion providers to meet such standards (see Targeted Regulation of Abortion Providers).
- Oklahoma adopted a measure allowing for unannounced and warrantless inspections of abortion providers; enforcement of the provision is blocked pending a legal challenge.
- A new Ohio law requires abortion providers to be within 30 miles of a hospital with which it has a formal transfer agreement (permitting the transfer of patients needing emergency care) and automatically denies clinics’ requests to waive provisions of the state’s TRAP law if not approved by the state Health Department within 60 days.
- Arkansas approved a measure requiring physicians who administer medication abortion to have a contract with another physician, who has admitting privileges at a local hospital, to handle emergencies, making it the only state to have such a requirement that applies only to providers of medication abortion. Five states require all abortion providers to have admitting privileges.
- Arkansas and Indiana adopted measures mandating specific and costly requirements for the disposal of tissue following an abortion. The Arkansas law requires the tissue to be handled in a “respectful and proper manner.” The new law in Indiana requires the tissue to be either cremated or buried in a cemetery.
Family Planning Providers
In the aftermath of the release of a series of deceptively edited sting videos aimed at Planned Parenthood, attempts to defund the organization have flared at both the federal and state levels. By the end of 2015, some 11 states had moved to slash funding either for Planned Parenthood health centers specifically or for any family planning provider that also offers abortion services. A Guttmacher analysis shows that defunding Planned Parenthood could seriously impair women’s access to needed services: In two-thirds of the 491 counties in which they are located, Planned Parenthood health centers serve at least half of all women obtaining contraceptive care from safety-net health centers. In one-fifth of the counties in which they are located, Planned Parenthood sites are the sole safety-net family planning center.
States have targeted a variety of funding streams on which family planning providers rely to fund the breadth of their services and activities, and are likely to continue in this vein in the upcoming 2016 legislative sessions:
- Medicaid
Mirroring events in Congress, five states—Alabama, Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma and Texas—took steps to exclude Planned Parenthood from the Medicaid program in 2015. These efforts were blocked by federal courts in Alabama, Arkansas and Louisiana; a challenge was just filed in November in Texas. (The initial Arkansas ruling applied only to the three Medicaid enrollees named in the suit; efforts are underway to expand that injunction to all enrollees in the state.) Similar efforts made by Arizona and Indiana in recent years were also rebuffed by federal courts.
- Other Family Planning Funding
Following the release of the videos, North Carolina expanded its existing provision blocking state funding of “non-public” family planning providers to explicitly apply to family planning providers that also offer abortion services. (Similar measures to bar funding for family planning providers that offer abortion care were introduced in Illinois, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin.) In addition, New Hampshire’s Executive Council, an administrative board charged with overseeing large funding streams in the state, excluded Planned Parenthood health centers from receiving federal Title X dollars that flow through the state. (Title X funding that Planned Parenthood receives directly from the federal government is not affected.)
Ten states limit eligibility for family planning funding (see State Family Planning Funding Restrictions). Eight of these states—Arizona, Arkansas, Colorado, Indiana, North Carolina, Ohio, Texas and Wisconsin—prohibit abortion providers from receiving state family planning dollars. Kansas and Oklahoma exclude family planning providers not operated by public entities from eligibility.
- Funding for Related to Services and Activities
North Carolina and Utah moved to exclude family planning providers from eligibility for funding for related services. Legislation enacted in North Carolina bars family planning providers that offer abortion services from receiving funding for adolescent parenting and teen pregnancy prevention programs. Utah Gov. Gary Herbert (R) directed the state department of health to discontinue any funding for Planned Parenthood health centers, including funding for STI surveillance efforts, STI testing and treatment and abstinence education; a federal appellate court recently barred the state from excluding Planned Parenthood from the funds.
Fetal Tissue Donation and Research
As yet another consequence of the release of the Planned Parenthood sting videos, 10 states moved to regulate either the process for fetal tissue donation or biomedical research conducted in the state using fetal tissue resulting from induced abortions. Fetal tissue research has been integral to many of the major medical advances of our age. For example, fetal cell lines were used in the development of the polio vaccine, a breakthrough for which the 1954 Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded. In addition, vaccines for diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, chickenpox, hepatitis A and rabies were all created using cell-line cultures originating from fetal tissue. In short, fetal tissue research has saved and improved the lives of millions of people worldwide.
During the final months of 2015, North Carolina and Arizona moved to regulate fetal tissue donation and research. A law enacted in North Carolina prohibits the sale of fetal tissue for a profit, paralleling federal requirements. Arizona adopted an emergency regulation requiring facilities to report any donation of fetal tissue to the state. Measures related to fetal tissue donation and research were introduced in Alabama, California, Michigan, New Jersey, Ohio, New York and Wisconsin.
Explore current state laws and policies on sexual and reproductive health topics.
Get an overview of state legislative and policy activity to date.